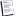
Glucose
The amount of glucose in the blood after a prolonged period of fasting (12-14 hours) is used to determine whether a person is in a hypoglycemic (low blood glucose) or hyperglycemic (high blood glucose) state. Both can be indicators of serious conditions. Increased levels can be indicative of diabetes mellitus, acute stress, Cushing's syndrome, chronic renal failure, corticosteroid therapy, acr*****ly, etc. Decreased levels could be indicative of hypothyroidism, insulinoma, liver disease, insulin overdose, and starvation.
Normal range:
Adult Male
65-120 mg/dl
Adult Female
65-120 mg/dl
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen)
This test measures the amount of urea nitrogen that's present in the blood. When protein is metabolized, the end product is urea which is formed in the liver and excreted from the bloodstream via the kidneys. This is why BUN is a good indicator of both liver and kidney function. Increased levels can stem from shock, burns, dehydration, congestive hear failure, myocardial infarction, excessive protein ingestion, excessive protein catabolism, starvation, sepsis, renal disease, renal failure, etc. Causes of a decrease in levels can be liver failure, overhydration, negative nitrogen balance via malnutrition, pregnancy, etc.
Normal range:
Adults
10-20 mg/dl
Creatinine
Creatinine is a byproduct of creatine phosphate, the chemical used in contraction of skeletal muscle. So, the more muscle mass you have, the higher the creatine levels and therefore the higher the levels of creatinine. Also, when you ingest large amounts of beef or other meats that have high levels of creatine in them, you can increase creatinine levels as well. Since creatinine levels are used to measure the functioning of the kidneys, this easily explains why creatine has been accused of causing kidney damage, since it naturally results in an increase in creatinine levels.
However, we need to remember that these tests are only indicators of functioning and thus outside drugs and supplements can influence them and give false results, as creatine may do. This is why creatine, while increasing creatinine levels, does not cause renal damage or impair function. Generally speaking, though, increased levels are indicative of urinary tract obstruction, acute tubular necrosis, reduced renal blood flow (stemming from shock, dehydration, congestive heart failure, atherosclerosis), as well as acr*****ly. Decreased levels can be indicative of debilitation, and decreased muscle mass via disease or some other cause.
Normal range:
Adult Male
0.6-1.2 mg/dl
Adult Female
0.5-1.1 mg/dl
BUN/Creatinine Ratio
A high ratio may be found in states of shock, volume depletion, hypotension, dehydration, gastrointestinal bleeding, and in some cases, a catabolic state. A low ratio can be indicative of a low protein diet, malnutrition, pregnancy, severe liver disease, ketosis, etc. Keep in mind, though, that the term BUN, when used in the same sentence as hamburger or hotdog, usually means something else entirely. An important thing to note again is that with a high protein diet, you'll likely have a higher ratio and this is nothing to worry about.
Normal range:
Adult
6-25
Calcium
Calcium is measured in order to assess the function of the parathyroid and calcium metabolism. Increased levels can stem from hyperparathyroidism, metastatic tumor to the bone, prolonged immobilization, lymphoma, hyperthyroidism, acr*****ly, etc. It's also important to note that anabolic steroids can also increase calcium levels. Decreased levels can stem from renal failure, rickets, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, pancreatitis, and alkalosis.
Normal range:
Adult
9-10.5 mg/dl
Liver Function
Total Protein
This measures the total level of albumin and globulin in the body. Albumin is synthesized by the liver and as such is used as an indicator of liver function. It functions to transport hormones, enzymes, drugs and other constituents of the blood.
Globulins are the building blocks of your body's antibodies. Measuring the levels of these two proteins is also an indicator of nutritional status. Increased albumin levels can result from dehydration, while decreased albumin levels can result from malnutrition, pregnancy, liver disease, overhydration, inflammatory diseases, etc. Increased globulin levels can result from inflammatory diseases, hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol), iron deficiency anemia, as well as infections. Decreased globulin levels can result from hyperthyroidism, liver dysfunction, malnutrition, and immune deficiencies or disorders.
As another important side note, anabolic steroids, growth hormone, and insulin can all increase protein levels.
Normal range:
Adult
Total Protein: 6.4-8.3 g/dl
Albumin: 3.5-5 g/dl
Globulin: 2.3-3.4 g/dl
Albumin/Globulin Ratio:
Adult
0.8-2.0
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is one of the many constituents of bile, which is formed in the liver. An increase in levels of bilirubin can be indicative of liver stress or damage/inflammation. Drugs that may increase bilirubin include oral anabolic steroids (17-AA), antibiotics, diuretics, morphine, codeine, contraceptives, etc. Drugs that may decrease levels are barbiturates and caffeine. Non-drug induced increased levels can be indicative of gallstones, extensive liver metastasis, and cholestasis from certain drugs, hepatitis, sepsis, sickle cell anemia, cirrhosis, etc.
Normal range:
Total Bilirubin for Adult
0.3-1.0 mg/dl
Alkaline Phosphatase
This enzyme is found in very high concentrations in the liver and for this reason is used as an indicator of liver stress or damage. Increased levels can stem from cirrhosis, liver tumor, pregnancy, healing fracture, normal bones of growing children, and rheumatoid arthritis. Decreased levels can stem from hypothyroidism, malnutrition, pernicious anemia, scurvy (vitamin C deficiency) and excess vitamin B ingestion. As a side note, antibiotics can cause an increase in the enzyme levels.
Normal range:
16-21 years
30-200 U/L
Adult
30-120 U/L
__________________
www.steroidscycles.net www.hypermuscles.com
Disclaimer: Hypermuscles.com does not promote the use of anabolic steroids without a doctor's prescription. The information we share is for entertainment and research purposes only.
|